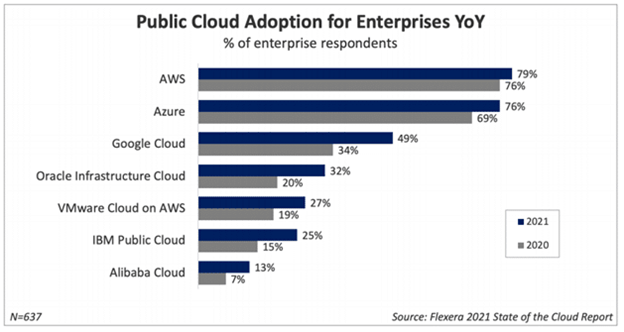
Cloud computing has become the go to solution for many businesses because of various benefits it offers. Enterprises continue to migrate workloads to the cloud (see image below). For organization looking to migrate on-prem software, data or infrastructure into cloud, the key task is to identify and concentrate on is the cloud enablement strategy.
Here’s a quick summary of key areas that need to be focused on for a successful cloud enablement strategy.
Define goals and expectations
Before embarking on the cloud migration journey, it is critical to define goals and the expectations of the end results. The end results can be in different forms, be it the reduction of costs, increased performance, higher availability or dynamic scalability. Migrating to cloud just because someone else did cannot be the driver for cloud enablement. Each organization must identify its drivers for migration to the cloud.
Assess requirements
Once the goals have been identified, it is important to perform an assessment of the current state on-prem setup, as well understand the challenges and roadblocks that may be encountered with cloud enablement of applications, data and infrastructure. This assessment can be done with a cloud partner or by the organization.
Select the cloud deployment model
There are three cloud deployment models, and each organization needs to choose the right deployment model for its needs. Each deployment model has associated pros & cons, that must be factored into the selection strategy.
- Public Cloud: All hardware, software and other supporting infrastructure are owned and managed by cloud provider
- Private Cloud: Consists of cloud computing resources used exclusively by one business or organization
- Hybrid Cloud: Combination of on-prem infrastructure or private cloud with a public cloud
Select the right cloud service provider
It is critical to select the right service provider as a part of the organization’s cloud enablement. Below are some key areas to consider when selecting a cloud service provider.
- Certifications & Standards: Certifications provide assurance to cloud service customers that their critical security requirements are met. Key areas to review are the existence of structured processes, effective data management, good knowledge management, and service status visibility. It is also critical to understand how the provider plans to resource and support continuous adherence to these standards.
- Technologies & Service Roadmap: Evaluating if the cloud service provider’s platform supports the technologies in the organization’s current environment, is an important step. Equally important is to understand the service provider’s long-term service roadmap and carefully validate if the roadmap suits the organization’s needs in long term.
- Data Security, Data Governance, and business policies: Governance policies & processes related to security and data governance should be an integral part of the provider assessment.
- Service Dependencies and Partnerships: Risks associated with engaging providers with a long chain of subcontractors, must be well understood. This could impact mission critical business processes or regulated data related processes.
- Contracts, Commercials & SLAs: Impact of contracts and commercial and service level agreements can have a downstream impact on an organization’s contracts with its end-customers. This impact must be evaluated as a part of the enablement strategy.
- Reliability & Performance: Understanding the provider’s established, documented and proven processes for dealing with planned and unplanned downtime directly impacts the organization’s ability to serve its end-customers.
- Migration Support, Vendor Lock in & Exit Planning: Vendor lock-in due to provider’s use of proprietary technology directly impacts an organization’s costs, and these risks should be carefully evaluated.
- Business health & Company Profile: Finally, understanding the provider’s current & past business performance, financials, acquisitions, divestments, legal challenges, etc. can provide insight into what to expect from the provider in the future.
Define the Architecture
A well thought and defined architecture means less issues while using services in cloud. There are three types of services offered in the cloud: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), Software as a Service (SaaS). Components in the cloud architecture can be a mix and match of these based on the organization’s assessment and requirements. It is recommended to choose the cloud native/PaaS services as much as possible, as they provide better scalability options, and organizations do not need to worry about maintenance of the underlying infrastructure and OS upgrades/patches. Here are some of the key steps to address when building out the appropriate cloud architecture.
- Identify all components involved in the current system and come up with an equivalent component in the proposed cloud architecture.
- Outline the security policies and put components in place to implement security.
- Determine the services enabled for public and internal use. Create a framework and associated policies that manage access for internal services.
- Create a network architecture to identify how all components are tied together and how the data flows across the end-to-end architecture.
About Encora
Fast-growing tech companies partner with Encora to outsource product development and drive growth. Contact us to learn more about our software engineering capabilities.

